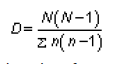Understandings:
- An indicator species is an organism used to assess a specific environmental condition
- Relative numbers of indicator species can be used to calculate the value of a established to justify a hierarchy of value of one species over another? biotic index.
- In situ conservation may require active management of nature reserves or national parks.
- Ex situ conservation is the preservation of species outside their natural habitats.
- Biogeographic factors affect species diversity.
- Richness and evenness are components of biodiversity.
Applications and skills:
- Application: Case study of the captive breeding and reintroduction of an endangered animal species.
- Application: Analysis of the impact of biogeographic factors on diversity limited to island size and edge effects.
- Skill: Analysis of the biodiversity of two local communities using Simpson’s reciprocal index of diversity.
Guidance:
- The formula for Simpson’s reciprocal index of diversity is:
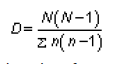
D = diversity index, N = total number of organisms of all species found and n = number of individuals of a particular species. |
Aims:
- Aim 8: Scientists supported by governments are devoting relatively large amounts of effort to save particular animal species. Can criteria be established to justify a hierarchy of value of one species over another?
|